Summarize this article with
Key Takeaways
VPN detection analyzes IP reputation, ASN ownership, traffic patterns, and historical behavior to flag masked locations.Residential and mobile proxies are harder to detect than data center VPNs.Device intelligence solutions like Fingerprint help identify repeat users even when VPN endpoints rotate.
VPNs, or virtual private networks, are a double-edged sword. On the one hand, they give users privacy and the ability to appear as if they’re in a different location. On the other hand, this anonymity can also be exploited by fraudsters.
VPNs are a simple way for fraudsters to masquerade as trustworthy users. They allow bad actors to mask their location, rotate through clean IP addresses, and sneak past basic security checks, like rate limits and geolocation blocks. Businesses need to be able to identify when someone is using a VPN to prevent abuse, spot high-risk sessions, and protect revenue.
In this post, we’ll break down what VPNs are, how they’re misused, and some effective techniques for VPN detection in the real world.
Evaluating vendors? Explore our analysis of the top VPN detection tools and how they differ.
What is a VPN and how do they work?
From a high-level perspective, a VPN works by routing a user’s internet traffic through a remote server, effectively hiding their real IP address behind the server’s IP address. This process encrypts the user's data and hides their true location from the websites they visit. With many VPN providers, users are even able to select the server location, whether it’s a different city or even a whole different country.
VPNs help by:
- Adding a layer of security when accessing a public resource over the internet
- Preventing anyone from packet sniffing or deep packet inspection on untrusted networks, especially when connected to an untrusted WiFi network or using unencrypted protocols like HTTP.
- Gaining anonymity, fighting censorship, or hiding the user's country of origin
While the above are legitimate reasons to use a VPN, they could also indicate suspicious behavior, like someone trying to hide a previously blocked IP address, making VPN detection an essential feature in fraud protection capabilities.
Why do people use a VPN?
VPNs are popular for many reasons including:
- Providing better data privacy when accessing unsecured public WiFi networks
- Enabling users to protect their data and hide their browsing activity from apps and websites that want to track them
- Offering more peace of mind for IT security teams at companies that allow employees to work remotely
- Allowing users to access region-restricted content or region-specific pricing
How fraudsters can misuse VPNs
While VPNs can be useful in helping users protect their privacy, they are also commonly used in fraud schemes such as:
Regional pricing fraud
Regional pricing is a way for businesses to charge different prices for the same goods or services based on where a customer lives. It’s a great way to both increase accessibility and maximize revenue by charging lower prices in lower-income regions and higher prices in more affluent regions.
Unfortunately, regional pricing fraud undermines this pricing model and makes it much less profitable for companies. With regional pricing fraud, bad actors use VPNs to hide their real location and dodge regional pricing rules. For example, those in higher-income areas can use VPNs to fake their IP addresses so they appear to be in a lower-income area to access cheaper prices for anything from airfare to streaming services — resulting in lost revenue for companies.
Evading regional restrictions
Businesses operating in regulated industries like iGaming and crypto to need to ensure they block access to visitors from restricted regions in order to avoid large fines or getting shut down completely. For example, gamblers may use VPNs to bypass sanctions that prohibit transactions from specific countries — and companies that don’t have an effective VPN detection solution in place to block that traffic could be leaving themselves wide open to regulatory action.
12 ways to detect VPN usage
VPNs can be detected through simple mechanisms like comparing the actual browser timezone with the target server's exit node or by using databases that store information about whether a given IP address belongs to the VPN. Or it could be based on more advanced methods like TCP/IP fingerprinting and other information present in the network traffic.
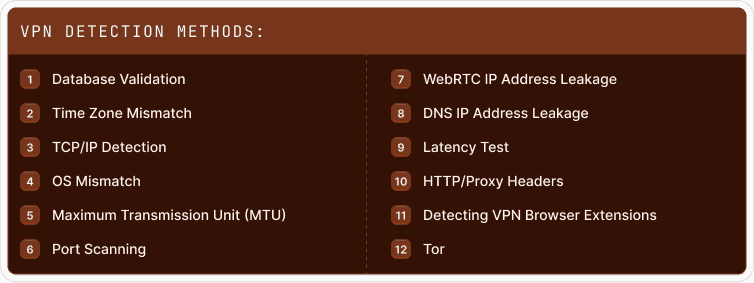
Here are some ways you can detect a user is using a VPN:
1. Database validation
IP address databases are a cornerstone in the arsenal of methods for detecting VPN use. These databases contain information about IP addresses, including their affiliation with known VPN or proxy services. Cross-matching a user's IP address with these databases can determine whether the user is associated with a VPN or proxy.
Several widely used IP address databases have gained widespread use in VPN detection. Services such as MaxMind, Udger, and IPinfo are known for their accuracy and extensive databases. These databases are constantly updating their information to ensure it is current. Despite their effectiveness in identifying the IP addresses of public VPNs and proxy servers, this method is unsuitable for detecting private self-hosted and corporate VPNs.
2. Time zone mismatch
Time zone mismatch detection uses the web browser API to display the browser's local time zone based on device location or system settings. When a visitor uses a VPN to connect to a server located in a different geographic region, this can result in a noticeable discrepancy between the time zone returned by the browser and the time zone of the geographic area of their IP address.
For example, for a website, a user located in New York City appears to be browsing the web from Tokyo because of the VPN server's location. This mismatch can be a sign of VPN or proxy use, as it shows an attempt to hide one's IP address. However, simply changing the time zone in the system settings is sufficient to pass it.
You can implement logic to detect impossible travel to improve the accuracy of time zone mismatch detection, which involves analyzing IP address changes between different regions and determining whether these changes occur in an unreasonably short period. For example, if an identified user's IP address suddenly goes from New York to Tokyo in seconds, this is a red flag.
3. Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) /IP detection
The technique of analyzing TCP and IP packets is far from new, but it remains an effective tool to solve the problem of VPN detection. Collecting and analyzing information about the attributes of the connection at different network layers makes it possible to gain knowledge about the properties of the client device, such as the type and version of the operating system, network configuration, and more. When these details don’t match what’s reported by the browser, it often indicates that the connection is being routed through a VPN or proxy.
It is possible to familiarize oneself with the implementation of these techniques with the help of several utilities. Tools like p0f and newer forks like satori offer passive packet-level analysis that observe the TCP/IP stack to guess the remote operating system, while tools like Nmap actively send a series of transport layer requests and match replies against a regularly updated signature database.
4. OS Mismatch
By analyzing the TCP/IP packets exchanged between the device and the web server, you can also discover the device's operating system, which indicates an OS mismatch when compared to the browser's operating system. Inconsistencies detected in this case may indicate the presence of a VPN, proxy server, or Apple's iCloud Private Relay.
It is also possible to recognize the operating system from the browser in different ways, for example, by parsing the user agent string or checking for unique JavaScript properties. Combining these methods will provide greater accuracy since spoofing of the user agent string is possible even with the built-in browser features, and some VPNs specifically modify packet headers, making it difficult to detect such differences.
5. Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU)
Having touched on the TCP/IP packet inspection, we should also talk about the method of determining VPN utilization by MTU values. Different VPN protocols, such as OpenVPN, L2TP, WireGuard, PPTP, etc., use different MTU values to optimize data transmission over network infrastructures.
For example, OpenVPN, a universal VPN protocol, allows flexible MTU customization. Users can modify MTU values according to specific network conditions, ensuring efficient data transmission. In contrast, protocols such as L2TP over IPsec or PPTP have predefined MTU values to ensure compatibility and reliability in different types of networks. However, it is possible to change the MTU.
While MTU analysis may indicate the use of a VPN, these values can also change by cause of legitimate network configuration or other factors unrelated to VPNs. Therefore, the detection process should consider the specific VPN protocol and its corresponding MTU values to minimize false positives and maintain accurate detection results.
6. Port scanning
Port scanning involves actively probing a user's device for open network ports, which could reveal the presence of a VPN or proxy. However, this method raises serious privacy issues, involving intrusive actions on a user's system without their consent, potentially violating their online privacy rights.
Furthermore, port scanning can result in false positives, misidentifying VPN users when ports are configured for legitimate reasons, such as corporate network setups or firewall configurations. Therefore, while port scanning may offer insights into VPN detection, its privacy-invasive nature and potential for inaccuracies make it a less ethical and less reliable option in this context.
7. WebRTC IP address leakage
WebRTC, being a critical technology for real-time communication, can inadvertently transmit the user's IP address, potentially compromising the user's privacy. However, using WebRTC IP address leakage as a VPN detection method is undesirable because modern browsers and some VPNs have mechanisms that reduce the likelihood of such leaks.
8. DNS IP Address Leakage
A DNS (Domain Name System) leak occurs when a user's DNS queries bypass the VPN tunnel, which can expose the user's real IP address. Although an IP address discovered due to a DNS leak can be helpful for VPN detection, these leaks are rare because many VPN providers use secure DNS servers to prevent such leaks.
9. Latency Test
Measuring network latency provides a method for determining VPN, but it is indirect and inaccurate. It can give false positives if users connect to geographically distant servers or have network performance issues unrelated to the VPN.
10. HTTP/Proxy Headers
Analyzing HTTP headers can reveal the use of VPN or proxy services. However, modern VPNs do not allow this method, and tech-savvy users can modify these headers to mimic non-VPN-related traffic, making this method less reliable.
11. Detecting VPN Browser Extensions
Discovering VPN extensions in the browser can detect VPNs, but it’s not complete, as many users use standalone VPN apps that hide the device's actual IP address for all traffic (whether from the browser or not), making this technique less effective.
Thus, while these methods can provide some insight into VPN detection, each has its limitations and can produce false positive or negative results. Combining multiple detection methods remains the most reliable approach to determine VPN usage and accurately minimize erroneous conclusions.
12. Tor
Tor is also worth mentioning. Tor, short for The Onion Router, is a well-known anonymity network. Detection of the Tor network involves recognizing the IP addresses associated with Tor nodes and output relays. Tor user traffic passes through a series of servers, and the IP address of the exit relay becomes visible when the user goes out to the open internet. Identification of these IP addresses can indicate the use of the Tor network.
Tor users are well aware of this detection method and often employ countermeasures to protect their anonymity. They may configure Tor bridges, use obfuscation techniques, or use VPNs, creating additional detection challenges. These countermeasures illustrate the constant cat-and-mouse game between privacy-conscious users and those trying to identify their browsing practices.
Maintaining user privacy and ethical data handling
VPN detection is useful for maintaining the security and integrity of your websites and apps. That said, legitimate VPN and Tor users care deeply about protecting their privacy and ensuring their data isn’t mishandled. Businesses need to ensure they make it clear they’re using VPN detection responsibly and in compliance with GDPR, CCPA, and ePrivacy regulations.
Being clear about what data you’re collecting, why it’s being collected, and how it’ll be used goes a long way. Avoiding invasive VPN detection techniques where possible (like port scanning) can also help to maintain user trust.
Most importantly, keep the following GDPR compliance principles in mind:
- Legitimate interest: Ensure you’re using fingerprinting and other VPN detection techniques for security-first use cases like fraud detection and account protection rather than user tracking.
- Data minimization: Collect only the minimum data necessary to detect VPNs.
- Transparency: Be transparent with users about VPN detection practices in your privacy policy.
Transparency and ethical data handling practices help maintain the loyalty of your more privacy-conscious users while also preserving the security of your site.
Why should you implement VPN detection?
Implementing VPN detection can help businesses better identify potentially suspicious users and protect their platforms. While using a VPN is not an immediate indicator of fraudulent intent, it can serve as an additional factor allowing for better protection against security and fraud threats.
Benefits include:
- Higher user identification accuracy: As mentioned earlier, VPNs can hide a visitor or user's actual location, making it harder to accurately associate the user with their account or previous sessions. VPN detection gives you a heads up on users who might be trying to avoid detection.
- Better website security: While not all VPN users are fraudsters, fraudsters do use VPNs when attempting fraudulent activities like account takeovers and bot attacks. VPN detection helps you keep your website secure by allowing you to block or limit access from suspicious IP addresses, reducing the risk of fraudulent activities. Additionally, you could block users using a VPN altogether if you want (but we don’t recommend this because you’ll likely also be blocking a large amount of legitimate traffic from privacy-conscious users).
- Enforced geo-based rules: When you are able to detect users changing their IPs with a VPN you are better able to protect geo-specific features, content, or pricing. Not only can this help protect profits but might also be a legal or regulatory requirement.
Highly accurate VPN detection with Fingerprint
Fingerprint is a device intelligence platform that analyzes your web or mobile visitors to accurately recognize devices and detect suspicious behavior, including VPN use, bot traffic, virtual machine use, and browser tampering.
Fingerprint provides over 20 Smart Signals that can give you an idea of user intent from their very first visit. With easy-to-use APIs and a wide variety of SDKs, detecting VPN use is as easy as making a single API call. No need to try and decipher and analyze the numerous amounts of potential VPN detection methods or figure out to combine them for the most accurate detection. Our researchers are constantly looking for new techniques and frequently update our platform so you don’t have to.
Final thoughts
VPN usage has drastically increased over the last few years: a recent Forbes Advisor poll in the UK found nearly half of respondents have used a VPN before, while another found 47% of Americans use VPNs. Comparatively, only a third of Americans had used a VPN just three years ago. This increase in usage represents a growing interest in online privacy, but also a growing security challenge for companies.
VPN detection is one of several tools in the fraud detection toolkit that can help businesses spot suspicious actors before they undermine the security of your website. Fingerprint offers VPN detection as part of its Smart Signals device intelligence offering and several other device intelligence signals, including IP blocklist matching and Browser Bot Detection. Smart Signals allows users to reveal the true intentions of every user with access to the most accurate real-time device intelligence available.
Ready to see how VPN detection can help solve your fraud challenges?
Test it out for yourself with a 14-day free trial!
FAQ
As for the accuracy of VPN detection, it can vary based on a number of factors. These can include the sophistication of the VPN service itself, the techniques being used for detection, and how up-to-date the company's information is regarding known VPN IP addresses. Some VPNs are better than others at disguising their traffic, and some detection methods are more effective than others. Additionally, if a company's database of known VPN IPs isn't regularly updated, it may fail to detect newer VPN services.