Browser fingerprinting is the foundation of device intelligence, enabling businesses to uniquely identify visitors to websites worldwide.
Understanding the various browser fingerprinting techniques is crucial for organizations wanting to enhance security and user experience. A highly accurate identifier, like a browser fingerprint, makes it easier for developers to triage suspicious traffic and restrict access to users attempting to hack into accounts, make fraudulent purchases, or spam your website. It also helps in tailoring user experiences while providing a more nuanced understanding of visitor interactions.
This article discusses browser fingerprinting, its common techniques, and its use for fraud prevention.
What is browser fingerprinting?
Browser fingerprinting is a set of tools and techniques that can capture data through a web user's browsing activity. Browser fingerprinting gathers information provided by the browser related to a user's operating system, browser type, screen resolution, time zone, keyboard layout, and more. Processing these details creates a unique identifier, or "digital fingerprint," for each browser. This identifier remains consistent across different browsing sessions, making it a reliable tool for visitor identification beyond the realm of traditional cookies, which can easily be cleared.
For businesses, browser fingerprinting offers significant advantages. It enables more accurate and stable visitor identification, which can be used to tailor visitor experiences, enhance reporting and fraud modeling, and improve the overall website experience. When a business is better able to recognize a visitor, it can optimize its websites and applications to better suit its audience's needs, improving visitor experience and overall website conversions. Additional benefits include:
- Fraud prevention. You can use browser fingerprinting to detect, mitigate, and block users with suspicious browser characteristics or who have engaged in fraudulent activities.
- Enhanced security. Browser fingerprinting uses real-time data to stop attacks and protect individual users' data and your business from revenue loss.
- Website optimization. Marketers and advertising technology companies can incorporate browser fingerprinting to hypertarget and hyperlocalize website traffic.
Fingerprinting vs. cookies
Cookies are small pieces of data stored within the user’s browser. You can use cookies to store a unique identifier hash in the browser the first time a visitor lands on your website. When a visitor has a cookie that matches a previous visit record in your database, then you can be confident that the two visitors are the same.
However, cookies are very easy to manipulate or delete. In cases where visitors delete or intentionally block cookies, browser fingerprinting provides an alternative means of effectively recognizing browsers with remarkable accuracy, as it does not rely on the storage of data on the user’s device.
Browser fingerprinting vs. device fingerprinting
Device fingerprinting goes further than trying to recognize a browser by trying to recognize the device the user is using, regardless of which browser or client they are using to access your site. While device fingerprinting can apply to many types of devices, it is more prevalent with mobile device identification, which gathers data about a user's device and combines the information to generate a unique fingerprint for each device. The signals available for mobile device fingerprinting differ from those retrieved in the browser and vary between iOS, Android, and other mobile operating systems. Mobile apps can then use these fingerprints to recognize devices even if the app cache or data is cleared.
How does browser fingerprinting work?
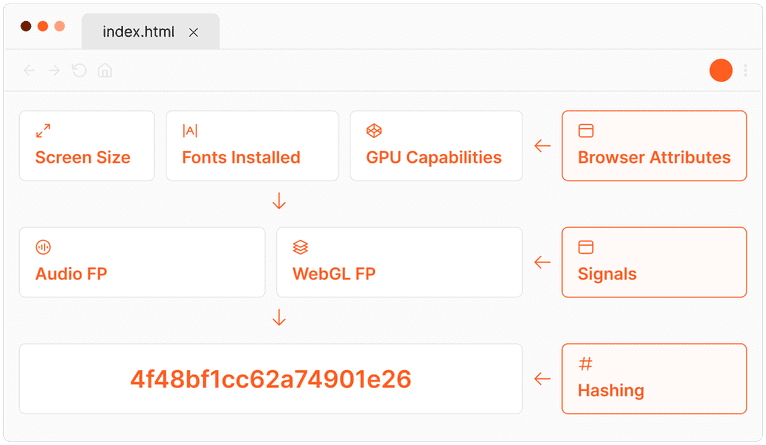
Browser fingerprinting operates on the principle of collecting and analyzing a variety of data points (or "signals") from a visitor’s web browser and device to create a unique identifier for that visitor. This process is meticulously designed to pinpoint the subtle differences between visitors’ browsers, even among those using identical device models or operating systems.
The effectiveness of browser fingerprinting lies in its ability to generate a high-entropy identifier, meaning that the collected data points create a sufficiently complex and unique profile that distinguishes one user from millions of others online.
For instance, while countless visitors might share the same operating system version, variations in installed software, browser configurations, and even minor hardware differences contribute to creating a distinct fingerprint.
Additionally, the signals need to be persistent, so one tiny change does not completely change the identifier. Good browser fingerprinting weighs different signals based on their uniqueness and durability to determine the generated fingerprint.
This approach allows for a level of precision in visitor identification that surpasses conventional identification techniques, making it a powerful tool for accurately recognizing site visitors without relying on more easily manipulated methods.
What information is gathered?
The signals or attributes used in this process include, but are not limited to:
- Type and version of the web browser
- Operating system and its version
- Screen resolution and color depth
- Installed fonts and plugins
- Time zone and language settings
- Use of ad blockers
See your own unique visitor ID using these signals with our browser fingerprint test
These signals are compiled through scripts running in the background when a user visits your website. These scripts meticulously examine the software and hardware configuration without altering or interrupting the user experience. The resulting "fingerprint" is a unique composite of these characteristics, forming a highly distinctive profile that can be used to identify the visitor across different browsing sessions. Importantly, this method remains effective even when traditional identification methods, like cookies, are bypassed through incognito browsing or cleared browser data.
Fingerprint’s technology employs several cutting-edge browser identification methods to gather over 100 individual signals. These signals are combined with server-side analysis and machine learning to generate a stable visitor identifier, providing a persistent and valuable abstraction of a browser fingerprint, even if a visitor changes settings or updates software on their device.
Is browser fingerprinting GDPR and CCPA compliant?
The compliance considerations for browser fingerprinting depend on the way it is being used. Under GDPR and CCPA privacy regulations, businesses are permitted to use browser fingerprinting to protect the security of their products and websites. This is seen as “legitimate interest” and does not have the same requirements as when used for personalization or tracking. Depending on your use of browser fingerprinting, you may be subject to certain disclosure or consent requirements.
Learn more about how Fingerprint ensures regulatory compliance.
How browser fingerprinting can be misused
While browser fingerprinting is an effective way to strengthen an online fraud prevention toolset, it can also be misused. Certain applications (not Fingerprint—we don’t track or collect PII) use fingerprinting to build detailed profiles of individuals and track their activity over time across multiple sites and sessions. This kind of surveillance raises ethical and regulatory concerns, especially since users typically don’t provide their consent to be tracked in this manner.
Privacy-focused browsers like Tor and Brave use countermeasures to combat abusive fingerprinting. For example, Tor encrypts data multiple times, routes traffic through at least 3 random relay nodes in its network, then peels off each layer of encryption at each node, providing ultimate anonymity. Brave actively blocks ads and trackers and offers an option to route traffic through the Tor network, further enhancing user privacy.
Balancing privacy and fingerprinting
Nearly any technology can be misused, no matter what it was originally designed to do. Fortunately, there are ways both users and businesses can prevent surveillance by bad actors and ensure compliance with privacy regulations.
For users
To bolster your online privacy:
- Use privacy-focused browsers (like Tor and Brave) that include built-in anti-fingerprinting protections.
- Disable JavaScript when possible to block some scripts that collect fingerprinting data. Note that this may likely hinder the experience of using the site.
- Limit the use of plugins and custom fonts, as these increase the uniqueness of your visitor ID.
- Avoid using unique browser configurations — these can introduce inconsistencies that make you easier to identify.
For businesses
To use browser fingerprinting responsibly and stay compliant with privacy regulations:
- Only use fingerprinting for security purposes, like fraud detection, account protection, or bot prevention.
- Include fingerprinting practices in your privacy policy and ensure they’re accessible and easy to understand.
- Respect “Do Not Track” and other privacy preferences when using fingerprinting data.
- Offer an opt-out for non-essential fingerprinting, like for personalization.
6 top browser fingerprinting techniques
There are several methods you can use to effectively create a fingerprint for a website visitor, including canvas fingerprinting, WebGL fingerprinting, media device fingerprinting, TLS fingerprinting, font fingerprinting, and audio fingerprinting. We discuss each of these methods in detail below.

Canvas fingerprinting
This browser fingerprinting technique uses the HTML5 canvas element to identify variances in a user’s GPU, graphics drivers, or graphics card. First, the script draws an image, often overlaid with text. Then, the script captures how the user’s web browser has rendered the image and text. Naturally, every device with different hardware and drivers will render the image slightly differently, slightly distorting its color and shape. A hash is then computed using the rendered image’s data, which serves as the ‘canvas fingerprint.’
Like any other browser fingerprinting technique, the scripts used for canvas fingerprinting operate in the background to keep the user from realizing that the fingerprinting is occurring. This fingerprinting technique is accurate and not too processing-intensive, making it one of the most employed script techniques.
To read more about this technique, read our article on JavaScript canvas fingerprinting.
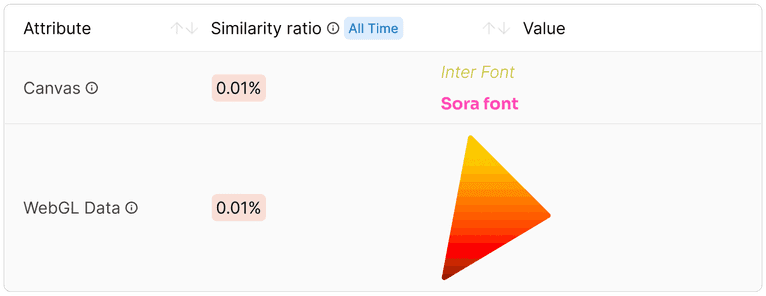
Canvas and WebGL rendered images from AmIUnique. Because of how this visitor's specific browser and device rendered these images, they can be narrowed down to a pool of fewer than 0.01% of total visitors.
WebGL fingerprinting
WebGL fingerprinting, an advanced subset of browser fingerprinting techniques, harnesses the power of the Web Graphics Library (WebGL) technology to render complex three-dimensional graphics directly in a user's web browser without the need for external plugins. WebGL fingerprinting operates by instructing the browser to create detailed, off-screen images that are then analyzed for unique characteristics. The way graphics are processed and rendered varies significantly across different combinations of graphics drivers, GPUs (Graphics Processing Units), and overall device hardware configurations.
The WebGL fingerprinting process begins with a script that commands the browser to generate a specific 3D graphic hidden from the user's view. The resulting image, while seemingly uniform in appearance, contains minute, hardware-dependent variations. These variations stem from the intrinsic differences in how individual devices’ GPUs and drivers interpret and execute the WebGL instructions.
For example, two devices with different models of GPUs or even different driver versions for the same GPU model will produce slightly different image outputs due to the variances in rendering algorithms and hardware capabilities. WebGL analyzes these subtle differences in the rendered images and then generates a unique identifier for each device.
Media device fingerprinting
Media device fingerprinting uncovers a list of all the connected media devices and their respective IDs on a user’s laptop or PC. This includes all internal media components like video cards, audio cards, and all connected or linked devices like headphones.
Media device fingerprinting is not widely used in fingerprinting functions because it requires the user to grant access to their microphone and camera to get a complete list of connected devices. However, this technique is helpful for services that inherently require webcam or microphone access, such as video chat services.
TLS fingerprinting
At its core, Transport Layer Security (TLS) is an algorithm that encrypts all your internet traffic, enhancing your online security. More specifically, TLS is a protocol that encrypts communications between a client and a server over the web, utilizing suites of cryptographic algorithms. Before utilizing TLS in communication, the client and server undergo a process known as the TLS handshake.
TLS fingerprinting is a technique that analyzes the specifics of how a client and server perform the TLS handshake, which is the initial step in establishing a secure communication channel over the web. By examining the unique combination of cryptographic algorithms and other parameters used during this handshake process, it's possible to generate a fingerprint of the devices or software involved.
To read more about this technique, read our article on TLS Fingerprinting.
Font fingerprinting
Font fingerprinting is a method used to identify users online through the unique set of fonts installed on their device. This technique involves websites executing scripts that assess which fonts are accessible on a visitor's computer, thereby generating a distinctive profile based on these fonts. Since individuals often have a diverse array of both system-default and personally installed fonts, this creates a specific fingerprint that can differentiate one user from another.
Font fingerprinting is particularly useful for web analytics and personalized content delivery, as it enables websites to identify returning users and understand their preferences without relying on traditional cookies, enhancing the user experience through customization.
Audio fingerprinting
Audio fingerprinting works by processing the subtle differences in how a device's software and hardware render audio content. When a sound is played on a device, factors such as the browser vendor and version, along with the CPU architecture, influence the exact way sound waves are generated and processed. These minute variations can be captured through a digital oscillator and analyzed to create a unique audio fingerprint of the device.
Audio fingerprinting can be particularly valuable for applications in digital rights management and content distribution, allowing platforms to manage how audio content is accessed and shared. Additionally, it can enhance user experiences by enabling more personalized audio content delivery based on the identified device characteristics.
Read our tutorial on how audio fingerprinting works using the Web Audio API to learn more about audio fingerprinting. You can also learn more about how it’s possible to bypass audio anti-fingerprinting protection in Apple Safari 17 here.
How browser fingerprinting can help detect fraud
Incorporating more than one browser fingerprinting technique plays a crucial role in creating a comprehensive and nuanced digital fingerprint. By combining signals from multiple sources, these methods achieve a high level of accuracy in browser recognition. This stability and accuracy are particularly valuable in the realm of fraud detection, where identifying and distinguishing between legitimate users and potential fraudsters is more important than ever.
Identifying fraudulent behavior
When working to detect and prevent fraud, it’s important to remember that only a small number of your site visitors are responsible for fraudulent activities. Because of this, your development team has to find a way to isolate these users to prevent them from abusing your platform.
However, you need to keep these security layers hidden from your trusted traffic since extra friction can cause unnecessary frustration for legitimate users, negatively impacting conversion rates and overall site engagement.
Bypassing traditional concealment techniques
Browser fingerprinting techniques are helpful for identifying visitors with a pattern of fraudulent behavior and then targeting only these visitors for additional security. In addition, fraudsters often use identity-concealing techniques like using a virtual machine, surfing through a VPN, or tampering with their browser. These are all areas where fingerprinting proves to be at its best since it identifies users quickly without relying on IP addresses and site cookies, and can also tell you when these techniques are in use.
Preventing account takeovers
One of the most common fraud types is account takeover, where malicious users try to hack a legitimate user’s account to make unauthorized purchases or steal their identity. With fingerprinting and related user identification technologies, additional security can be added to the login process for suspicious traffic only, making it more difficult for fraudsters to log in and take over trusted users’ accounts, even when credentials have been compromised in a phishing or social engineering scam.
Combating brute force and bot attacks
Incorporating browser fingerprinting techniques can significantly enhance the security measures against brute force and bot attacks. By identifying unique browser fingerprints, websites can detect and flag repetitive login attempts that exhibit patterns typical of automated bots or brute force strategies, even before the set threshold for failed attempts is reached.
Harness the power of browser fingerprinting with Fingerprint
The cornerstone of combating online fraud lies in the precision of visitor identification technology, which allows businesses to quickly distinguish between legitimate users and potential threats. Companies can protect their website from fraudulent activity and provide a secure and seamless experience for their trusted users while isolating and mitigating bad actors.
Ready to learn how Fingerprint’s visitor identification can help you identify suspicious activity faster? Contact our team to find out how to protect your website from fraudulent activity while complying with stringent privacy and data protection regulations.
Ready to combat online fraud?
Explore how Fingerprint can empower your business to enhance security and user experience.
FAQ
Browser fingerprinting and cookies serve similar purposes in identifying and tracking user behavior online, but they operate in fundamentally different ways. Cookies are small pieces of data stored on the user's device by websites to remember the user's actions and preferences over time.
In contrast, browser fingerprinting collects information about a user's device and browser settings (such as screen resolution, operating system, installed fonts, and plugins) to create a unique "fingerprint." Unlike cookies, which can be easily deleted by users, browser fingerprints are more challenging to alter because they are derived from the characteristics of the user's device and browser.
While completely avoiding digital fingerprinting is challenging due to its reliance on various aspects of a user's device and browser, users can take steps to minimize their uniqueness and make identification more difficult.
Using privacy-focused browsers or extensions that specifically limit fingerprinting techniques can help obscure or randomize the information shared with websites. Regularly updating software and using common screen resolutions can also reduce the distinctiveness of a device's fingerprint.
Additionally, employing virtual private networks (VPNs) and browsing in incognito or private modes can offer additional layers of privacy, although these measures may not fully prevent fingerprinting.
Browser fingerprinting is primarily designed for fraud detection, which generally does not require consent under most privacy laws. However, the extent to which you may need consent depends on where and how you choose to implement and use browser fingerprinting technology. We recommend working with your legal team to determine how best to address legal and compliance requirements.