Summarize this article with
The rise of vibe coding in 2025
Vibe coding is all the rage lately. If you’re (somehow) unfamiliar with the term, it’s the act of using an AI tool to code and build an application for you. Basically, anyone with an idea can type out a few prompts and spin up an app, launch a product, or start a side hustle without needing to write any code themselves.
These tools are fast, fun, and seem almost magical as you watch your ideas come to life on the screen. But here’s the thing: most vibe coders aren’t developers or even technical. And while this new technology breaks down barriers and makes app building something anyone can do, it also means the apps they generate don’t necessarily follow the best security practices. When you let AI take the wheel, it tends to skip over the boring (but essential) parts like security, leaving plenty of gaps just waiting to be exploited by folks up to no good.
And this isn’t just hypothetical. There are numerous examples out there of people having their vibe-coded apps hacked:
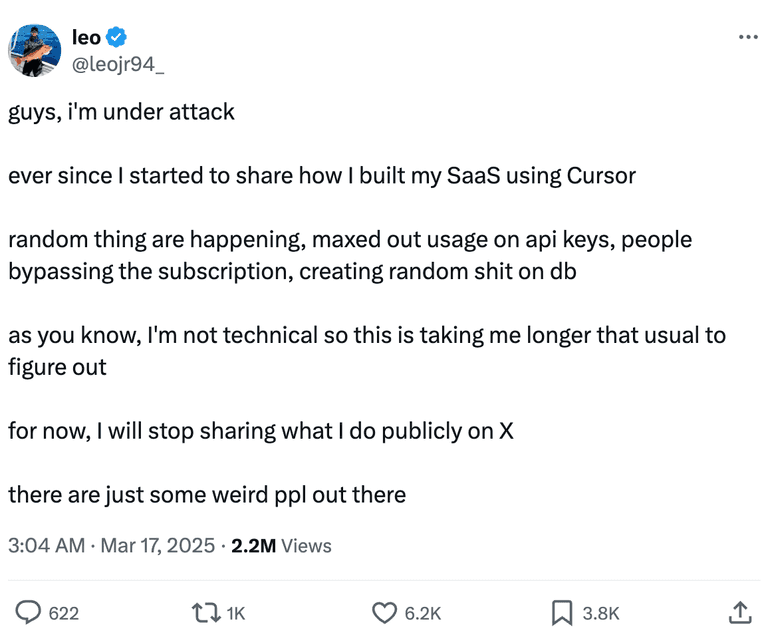
Or creating something they don’t know how to fix:
Those are the folks I’m hoping to help with this checklist. The people who want to take advantage of these amazing new technologies, but still build safely. Use this list as a starting point to confirm (or at least ask your AI tool to double-check) some security essentials before you hit “deploy” on the app you just vibe-coded into existence.
Want to build fast and stay secure? [Start a free trial](https://dashboard.fingerprint.com/signup) to add frictionless device intelligence to your vibe-coded app.
The hidden security risks of vibe coding
Security holes in AI-built apps are more common than most people realize. Take the Tea app, for example. The team left an entire cloud image bucket open to the internet, leaking tens of thousands of personal photos and ID documents. Though it hasn’t been confirmed to be a vibe-coded app, it sure smells like it. That kind of “oops” moment isn’t the result of some elite hacker attack; it’s what happens when security gets left out of the conversation entirely.
The numbers make it even clearer. According to a recent report, nearly seven in ten developers have discovered vulnerabilities introduced by AI-generated code, and one in five reported that these flaws led to serious incidents with real business impact. That’s not just a few bugs here or there; that’s data leaks, service outages, and revenue loss. And even if AI doesn’t burn the house down, it still creates a mess. Sixty-six percent of developers say they now spend more time fixing “almost-right” AI-generated code than writing their own.
Vibe coding makes it easy to ship fast, but just as easy to ship something fragile. Without understanding what’s safe, compliant, or potentially exposing user data, you could end up building a liability instead of a successful product.
The vibe coding security checklist
All right, now for the part that saves you from waking up to an “uh oh” email from your hosting provider. This checklist isn’t meant to turn you into a security engineer, but it’ll help you catch some common mistakes before you launch. You should confirm that each one is being handled appropriately. Either verify it yourself or ask your AI tool to explain how it’s being done in a way that allows you to inspect it. If the AI can’t show you, it probably didn’t do it.
Data handling
Validate all inputs on the backend to block malformed or malicious data.
Anything a user can type, upload, or submit should be treated as if it’s trying to break your app. Start by validating inputs. Every form, query, and request needs clear rules for what’s allowed. If you expect an email address, check that it’s actually an email address. If you expect a number, reject anything else. Don’t rely only on front-end validation; make sure your backend enforces it too.
Restrict file types and sizes, and store uploads outside your main app directory.
File uploads are another common weak spot. Only allow certain file types, set a maximum file size, and store uploads outside your main app directory. Never trust file names or paths provided by users; they’re easy to manipulate and can expose sensitive parts of your system.
Use parameterized queries to prevent SQL injection attacks.
Next, check how your app talks to its database. SQL injection is one of the oldest and easiest attacks to pull off. It happens when someone sneaks database commands into an input field to trick your app into running them. Make sure your AI-generated code uses parameterized queries or prepared statements instead of string concatenation.
These checks stop attackers from injecting SQL or scripts, prevent bad data from crashing your app, and block oversized or malicious uploads that could eat up resources or expose user data.
Escape HTML in user content to stop cross-site scripting (XSS).
Finally, sanitize your output. When your app displays user-generated content, escape HTML characters to prevent cross-site scripting (XSS). XSS happens when an attacker injects malicious scripts into pages viewed by other users, allowing them to steal cookies, perform actions on behalf of others, or display fake content. If your AI built a template or component that prints user input directly into the page, make sure it escapes that content properly. One unchecked field is all it takes to compromise your users.
Authentication and session security
Use strong authentication with salted password hashing and optional MFA.
Authentication is hard, and you probably shouldn’t try to roll your own. Always use a reputable library or service for handling credentials. If you insist on doing it yourself, make sure any stored passwords are hashed and salted. Hashing turns a password into a one-way value that can’t be reversed, and salting adds randomness to protect against rainbow table attacks, where precomputed lists are used to crack hashed passwords. If your AI tool wrote your auth system, confirm it isn’t storing passwords in plain text. If possible, add multi-factor authentication (MFA), since it’s one of the easiest ways to prevent account takeovers.
Enforce access control checks on every route, not just at login.
Next, apply access controls beyond the login page. Authentication confirms who someone is, while authorization determines what they can do. Every sensitive route or admin action should verify that the user has permission to access it. Without these checks, anyone who’s logged in (or worse, anyone who can guess a URL) could access data they shouldn’t.
Mark cookies as HttpOnly, Secure, and SameSite to protect sessions.
Also, make sure to protect your sessions with secure cookies. Set cookies to “HttpOnly” so JavaScript can’t read them, “Secure” so they’re only sent over HTTPS, and “SameSite” to reduce cross-site request forgery (CSRF) risks. Skipping these flags leaves your sessions vulnerable to hijacking or unauthorized use.
Use device intelligence to add an additional layer of protection.
In addition to these steps, using Fingerprint adds another layer of protection to your authentication system. Each device gets a unique visitor ID, helping you recognize returning users even if they clear cookies or switch browsers. Smart Signals provide extra context by detecting things like automation, virtual machines, or mismatched network details. These signals can help you block suspicious logins, detect session hijacking attempts, and flag risky behavior before it turns into account abuse.
Infrastructure and configuration
Force all traffic over HTTPS and block insecure HTTP requests.
Your app’s infrastructure and configuration set the foundation for its security. Start by forcing all traffic over HTTPS. HTTP sends data in plain text, which means anyone on the same network can intercept or alter requests. Redirect every HTTP request to HTTPS and make sure your SSL certificate is valid and renews automatically. Thankfully, many hosting providers do this for you, though you may need to change settings to ensure it’s always enforced.
Store secrets in environment variables or a secrets manager, never in code.
Store secrets like API keys, database passwords, and access tokens in a safe location and never commit them to source control like GitHub. They should live in environment variables or a secrets manager, never hard-coded in your codebase. If your AI tool generated your project, check that it didn’t sneak credentials into a random config file that’s being committed.
Require authentication and proper CORS settings for all API endpoints.
Extending a bit on the authentication steps mentioned above, also secure your APIs. Every endpoint should require authentication and define strict CORS settings. CORS settings control which external domains are allowed to interact with your API and what types of requests they can make. Avoid using a wildcard “*” origin in production and limit access to trusted domains only. This prevents data exposure through unapproved clients or cross-site attacks.
Regularly update dependencies and remove unused or vulnerable packages.
Outdated or abandoned packages are one of the fastest ways to get compromised. Update regularly, run security audits, and remove anything you’re not using. According to a report by Endor Labs, 49% of the dependencies added by AI coding agents contain known vulnerabilities. Even a single stale dependency can open a hole in your app.
App behavior and resilience
Add rate limiting to prevent abuse and brute-force attacks.
Add rate limiting to protect your endpoints from brute-force logins, credential stuffing, or denial-of-service attempts. Set reasonable thresholds based on user actions, like login attempts, form submissions, or API calls, and respond with temporary blocks or delays when limits are hit. To go a step further, use device intelligence tools like Fingerprint to accurately identify repeat abusers even if they change IPs, clear cookies, or switch browsers. Combining rate limits with device-level identification helps you block persistent attackers without disrupting legitimate users.
Log only what’s necessary and never include secrets, tokens, or personal data.
When something breaks, don’t hand attackers extra information. Show users generic error messages like “Something went wrong” and keep detailed stack traces or database errors in your private logs. Those details can reveal technologies, file paths, or query structures that make an attacker’s job easier. At the same time, log only what’s necessary to debug or investigate issues. Never record passwords, tokens, or personal data, and avoid dumping entire request bodies. Assume your logs could one day be seen by someone else, and write them accordingly.
Good vibes only
Vibe coding is one of the coolest ways to bring ideas to life fast. But moving fast shouldn’t mean skipping the basics of security. A little awareness about input validation, authentication, API security, and session handling goes a long way toward keeping your app and your users safe.
The checklist in this guide gives you the essentials to confirm or ask your AI to verify before you hit deploy, so your next project ships with fewer surprises and more confidence. At the end of the day, no matter how capable your AI tool seems, you need to stay in control of what it builds and how it protects your users.
If you’re ready to go beyond the basics, Fingerprint can help. Our device intelligence platform adds another layer of defense with unique visitor identification and Smart Signals that catch suspicious activity early. If you want to talk about how we can make your vibe-coded app more secure, get in touch with us.
Ready to secure your vibe coded creation?
Install our JS agent on your website to uniquely identify the browsers that visit it.
FAQ
Without security checks in place, you risk exposing user data, losing customer trust, and creating easy entry points for attackers. A single overlooked input or misconfigured API can lead to serious breaches or downtime.
Common mistakes include skipping input validation, storing secrets unsafely, leaving API endpoints exposed, and using weak or incomplete authentication setups.
No, this list is just a starting point. Real security requires continuous review, updates, and testing; it’s not a one-time task. Still, these checks cover many of the pitfalls vibe coders often miss and provide a solid foundation.