Summarize this article with
Firefox is a popular, fast, and reliable web browser that prioritizes users' safety on the internet with several security and privacy features.
In this article, you'll learn about Firefox's privacy and security features. You'll also learn how these features affect device identification, an essential part of improving Internet security.
Firefox's Privacy Features
Privacy features allow you to keep your personal data, internet behavior, web browsing history, and more private.
Firefox offers various privacy settings. Some of them are enabled by default, while others can be enabled. You can change the default privacy settings in the web browser settings in the Privacy & Security section.
Enhanced Tracking Protection
The vast majority of websites collect information about users' online behavior and preferences. This information is used without users' consent to create user profiles, which are sold to third-party companies so that they can create personalized advertisements for their products and services.
Firefox's enhanced tracking protection feature allows you to block the trackers that collect your information as you use the internet. Enhanced tracking protection also includes the ability to automatically detect and block dangerous scripts.
Enhanced tracking protection has three modes: standard, strict, and custom. Standard is the default mode.
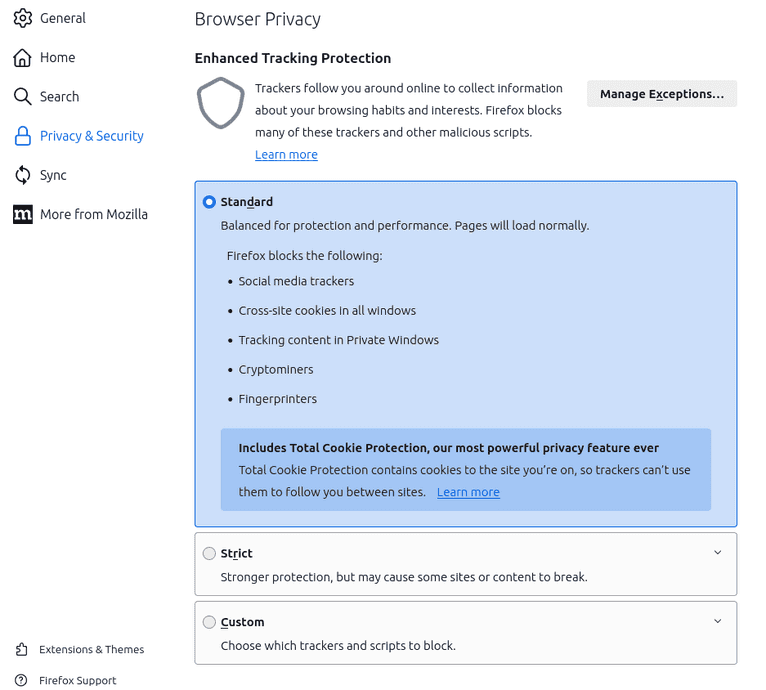
Even though standard mode blocks social media trackers, cross-site cookies in all windows, tracking content in private windows, and cryptominers, it doesn't affect the performance and operation of sites.
Strict mode protects against all the above and blocks tracking content in all windows. Using this mode may cause the site to run slowly or crash. If this happens, it's recommended to choose the standard mode. Alternatively, you can disable enhanced tracking protection for that site only.
Custom mode allows you to choose which trackers to block—for example, choosing to allow trackers and scripts from Google but not from Meta. This is important for people with specific preferences towards vendors, or for digital analysts, advertisers, and front-end developers who want to test adtech implementations on a vendor-by-vendor basis.
Do Not Track
Firefox's Do Not Track feature allows you to notify websites that you do not want your behavior to be tracked. However, websites are not required to comply with this setting. It only informs them of your preferences.
By default, this feature is disabled.

Cookie and Cache Management
Your browser may store data such as images, scripts, and other files from the websites you visit on your device to allow websites to load faster. It also creates cookies that may contain sensitive information to help personalize and improve the browsing experience.
Regularly clearing your cache and cookies not only cleans up disk space; it also removes sensitive information so that attackers can't get hold of it.
Firefox lets you see how much memory cache and cookies take up on your device and delete them.

Clearing website data doesn't affect the performance of your device or browser. However, deleting cookies may log you out of websites, and clearing your cache may cause websites to load more slowly.
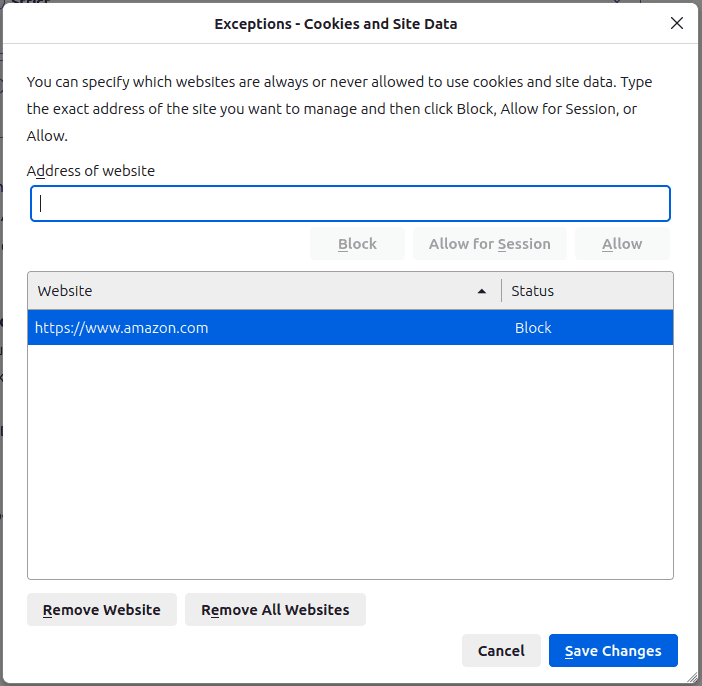
Firefox also allows you to maintain some exceptions. You can either exclude certain sites' cookies and site data from being cleared or always prevent sites from using cookies and site data.
Password Management
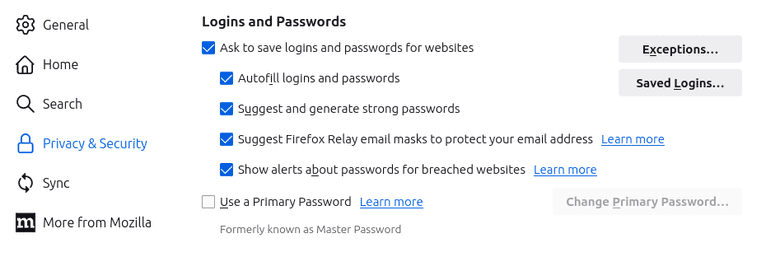
Firefox lets you save logins and passwords for websites and complete them automatically at the next login. These options are enabled by default.
Passwords are stored securely on your device in encrypted form and are not shared with third parties. If Firefox knows that any of your saved logins or passwords have been compromised, you can ask to be notified.
As with cookies and cache management, you can also exclude certain websites from password management so that their passwords are not saved.
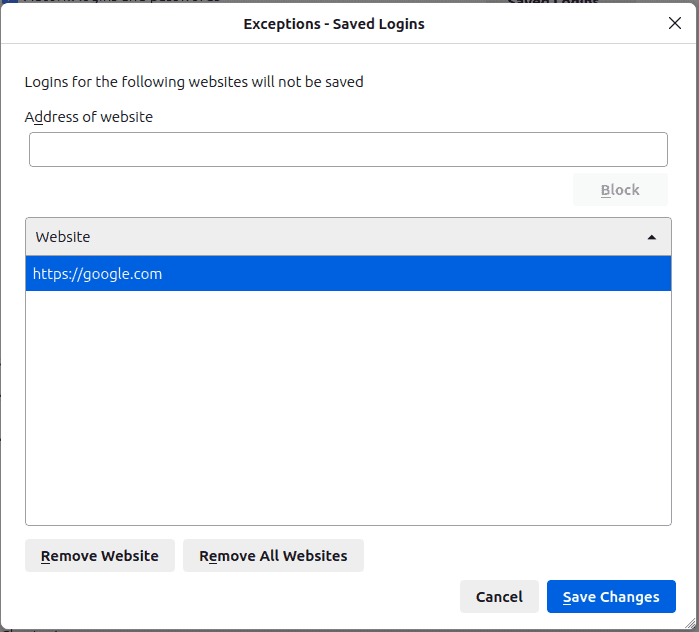
For additional protection of your confidential data, the primary password function allows you to set a password that's requested in every Firefox session requiring access to saved passwords. If, for example, someone else gets access to your device, this feature ensures that they can't access your passwords.
Primary passwords are set separately for each device, and they're not synchronized.
Browser and Search History
By default, Firefox saves your browsing history, downloads, forms, and searches.
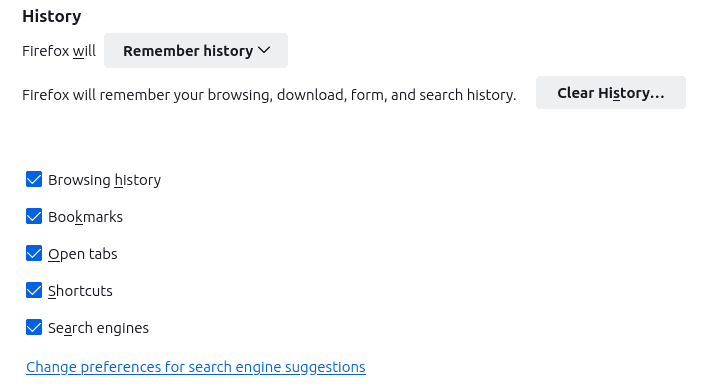
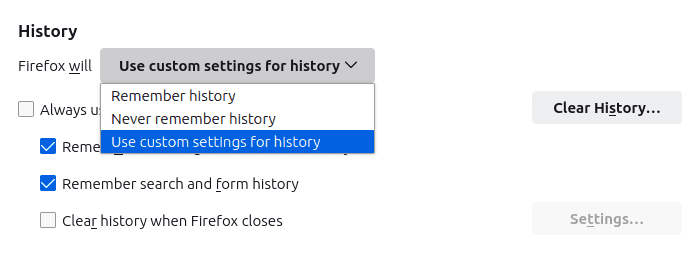
You can choose that it never saves your history, or you can enable custom settings for saving your history.
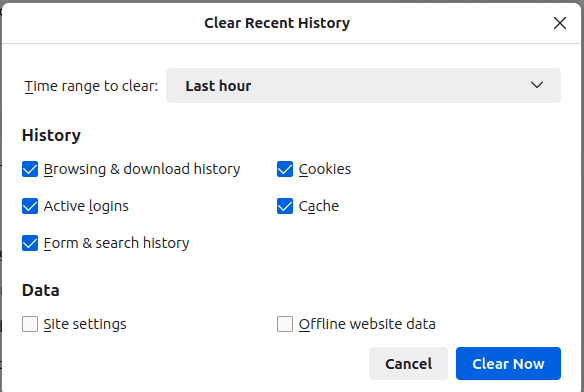
To ensure privacy, you can also delete saved data for all time or a certain interval and select the types of data you want to delete.
Browsing in Private Mode
If you're browsing in private mode, Firefox doesn't save the history of the sites you visit, and it doesn't store cookies after you close a browser window.
Using private mode doesn't make the browser more secure, but it enables you to isolate your activity from your regular browser use. A private session therefore makes it harder for websites and trackers to stitch your behavior to a potential profile they have on you. It also hides your browsing history from others who might use the same browser on that device.
Firefox's Security Features
Firefox's security features protect you from the theft of sensitive data and various types of attacks, including phishing and malware. You can change the security settings in the Privacy & Security section of the browser settings.
Handling of Secure Connections
HTTPS is a secure protocol that transfers data between the browser and the server in encrypted form to protect your data from theft and alteration. It's especially important for sites that require sensitive information, such as passwords and credit card details.
Firefox can enforce a secure connection in HTTPS-only mode. This means it checks if a request uses the HTTPS protocol. If not, Firefox tries to upgrade it. If the server does not support HTTPS, Firefox will display a full-page warning that the connection is not secure.
HTTPS-only mode is disabled by default in Firefox, but you can enable it for all windows or only for windows in private mode.

If a website that you trust does not support HTTPS connections, you can also add it to an exceptions list.
Phishing and Malware Protection
By default, Firefox provides advanced security features that protect you from phishing and malware. It's recommended to keep them on.

Before loading a website, Firefox checks whether it is on Firefox's list of unsafe sites. If it is, Firefox will block it and send you a notification. Firefox also checks the application files that you download and blocks dangerous downloads.
Add-ons and Extensions
You can improve your browser security even more with add-ons and extensions. For instance, ad blockers not only block unwanted ads but also improve security since the trackers that monitor your browsing behavior often hide in scripts that also load advertisements. Firefox blocks some ads by default, but you can enhance it with an extension like AdBlocker Ultimate.
Another useful add-on is Facebook Container, which isolates your activity on the Facebook site from other Internet activity so that Meta can't connect your browsing data with your profile.
NoScript Security Suite allows you to block JavaScript, Flash, and other executables that may contain malware and harm your computer. It also provides technologies to protect against cross-site scripting attacks (XSS), cross-zone DNS rebinding / CSRF attacks (router hacking), and clickjacking attempts.
However, you should be careful with the permissions you grant to extensions. Even though Firefox security specialists do check all add-ons and extensions before approval, you should also check that the description of every extension explains why it needs certain permissions and that it matches the features of the extension.
Device Identification
Since many browsers, browser extensions, operating systems, and VPNs block trackers, it has also become more difficult for businesses to identify malicious users for legitimate reasons like preventing fraud or identifying practices like account sharing that are against their terms.
One popular technique that's emerged as an alternative, device fingerprinting, collects a set of device properties like screen width, browser extensions, and user agent to create a so-called fingerprint that can be used to identify users' devices.
Unfortunately, fingerprinting is not only used for legitimate purposes like preventing fraud. It can also be used for the type of user tracking ad tech platforms are infamous for and that browsers like Firefox try to prevent.
However, unlike most privacy-minded browsers that mess with the fingerprint itself—Brave uses farbling, for example—Firefox blocks all requests that are known to have fingerprinting capabilities altogether. This technique allows parties that aren't known to have fingerprinting capabilities—such as the website itself—to use it.
Conclusion
Mozilla has made privacy a core feature of its browser, Firefox. The browser’s privacy and security features and settings protect against unwanted tracking, enforce secure connections, and enable users to keep their browsing behavior private. By default, Firefox blocks all connections to known trackers, preventing them from setting cookies or fingerprinting the device.
While Mozilla has taken a firm stance against fingerprinting, its anti-fingerprinting approach of blocking requests known to have fingerprinting capabilities allows websites to use fingerprinting for legitimate uses like fraud prevention.
If you're looking for a device identification vendor with an excellent reputation and high identification accuracy, consider Fingerprint. It supports all major browsers, including Firefox, and you can sign up for a free trial to try it out.
FAQ
Firefox checks websites against a list of unsafe sites and blocks downloads from malicious sources, notifying users to protect against phishing and malware.
Firefox's Private Browsing mode prevents the browser from saving the history of visited sites, cookies, and searches, isolating session activity and making it difficult for trackers to profile users.
Enhanced Tracking Protection blocks social media trackers, cross-site cookies, tracking content, and cryptominers in various modes (standard, strict, custom) to prevent unwanted tracking and enhance user privacy without significantly affecting site performance.